Chapter 4 Metabolite Annotation
The part provides an easy-to-use annotation function for unknown features or compounds. It consists of two functions in this part. One is feature match, which supports searching database with measured m/z and CCS for annotation. The second function is candidate rank, which can be in conjunct with any other annotation tools, such as MetFrag, CFM-ID, MS-Finder, and SIRIUS etc. With the results from previously mentioned tools, and inputting experimental m/z and experimental CCS, users can filter/re-rank candidates for more accurate annotation.
4.1 Feature to candidates (Feature match)
Feature match function provides a simple and straightforward way to annotate features with experimental m/z and CCS in the AllCCS database. There are several annotation conditions set in this part (Figure 4.1).
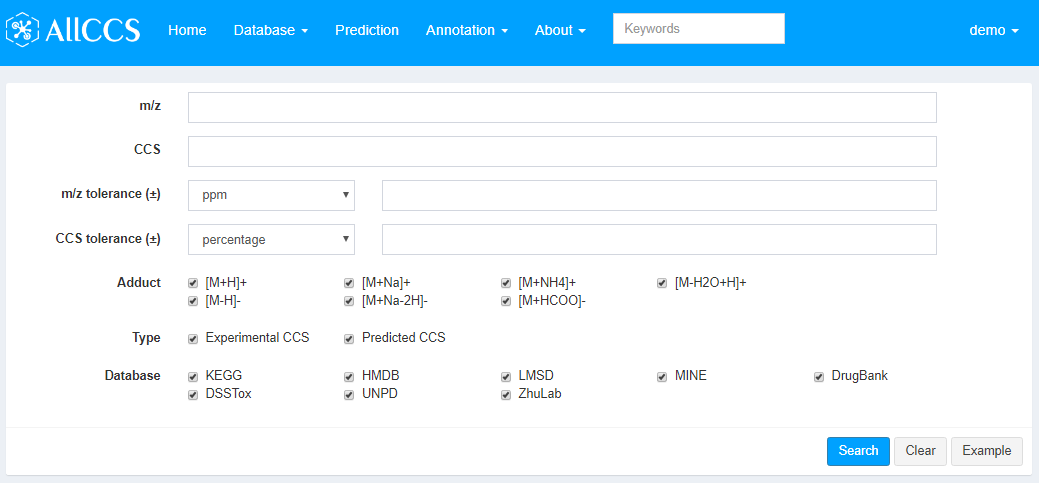
Figure 4.1: Feature annotation
- m/z: Experimental m/z of your interested peaks.
- CCS: Experimental CCS of your interested peaks.
- m/z tolerance (±): The tolerance between experimental m/z and theoretical m/z in database. Users can choose ppm or Dalton as unit.
- CCS tolerance (±): The tolerance between experimental CCS and theoretical CCS in database. Users can choose percentage or Å2 as unit.
- Adduct: Match with the checked adduct forms that exist in the database.
- Type: Match with the checked CCS type in the database, including Experimental CCS, Predicted CCS (See Section 2.1).
- Database: Match with the checked database. It includes 8 compound structure sources (See Section 2.1).
The match results are as follows (Figure 4.2). The results contain brief information for each compound as section 2.1 Compound Browser mentioned.
Users can check the interested compounds in the last column. Click the download option, you could download a CSV table containing the information of you checked compounds (Figure 4.2).
Note:
- Download function supports up to 100 items for one time.
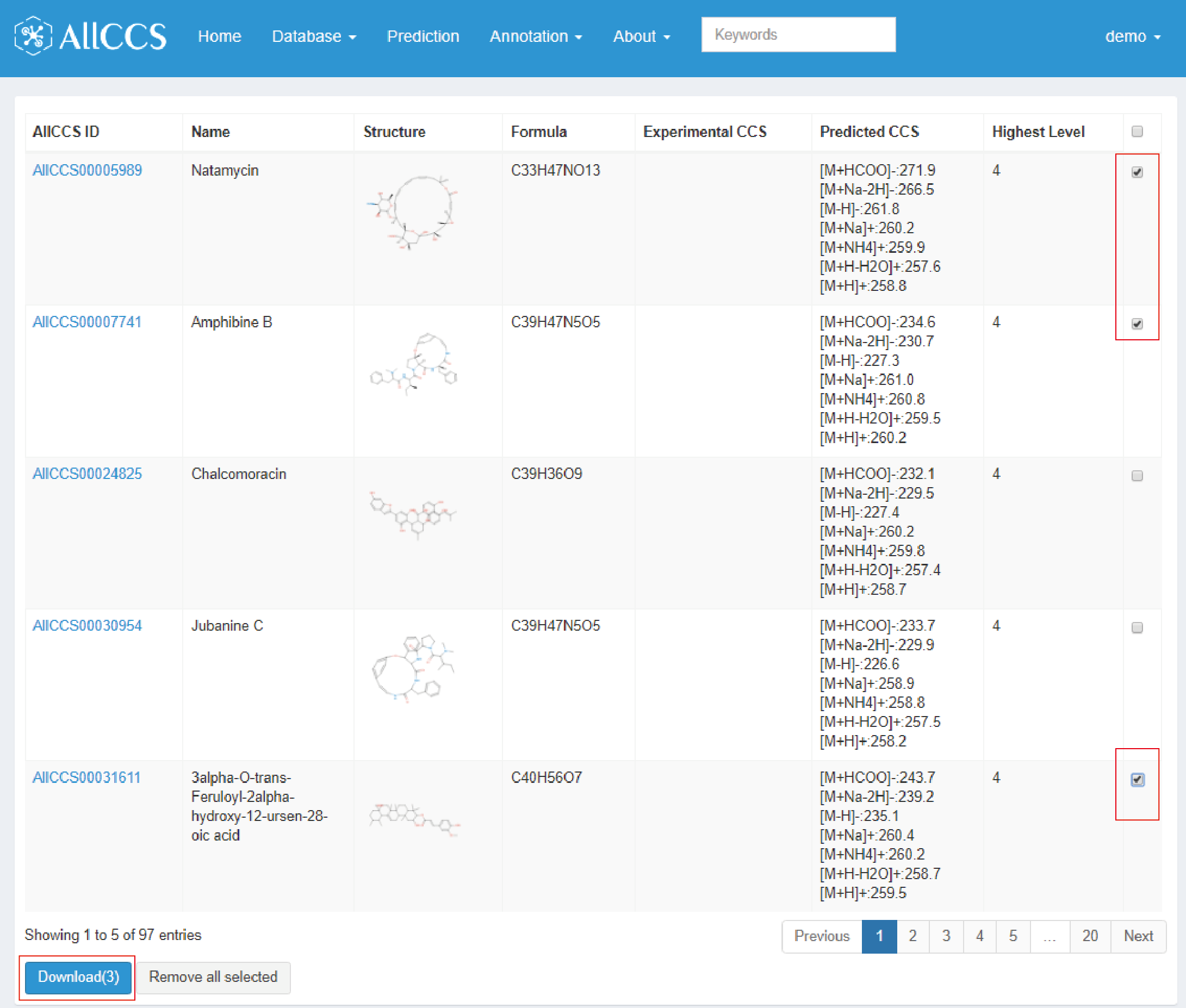
Figure 4.2: Feature match results
4.2 Complement to MS/MS result (Candidate rank)
The candidate rank function supports filtering/re-rank candidates with inputted candidate list. This function could be in conjunct with any other in-silico MS/MS tools like MetFrag, CFM-ID, MS-Finder, and SIRIUS etc. Specifically, it has two rank types: CCS filtering and CCS scoring. CCS filtering excludes candidates which CCS errors (comparing with predicted CCS values) beyond the pre-defined cutoff value. CCS scoring generates an integrated score for each candidate with custom weights of CCS score (The detail is some with our previous publication - LipidIMMS Analyzer (Zhou et al. 2019)) and MS/MS score. With CCS filtering or scoring, it can provide more credible results.
4.2.1 Data preparation
The MS/MS results (CSV file) generated from other tools should be modified as specific format. A demo data is showed in Figure 4.3. It should include 7 columns with specific names (“rank”, “name”, “smiles”, “inchikey”, “adduct”, “score”). The definitions of each column are given as follows:
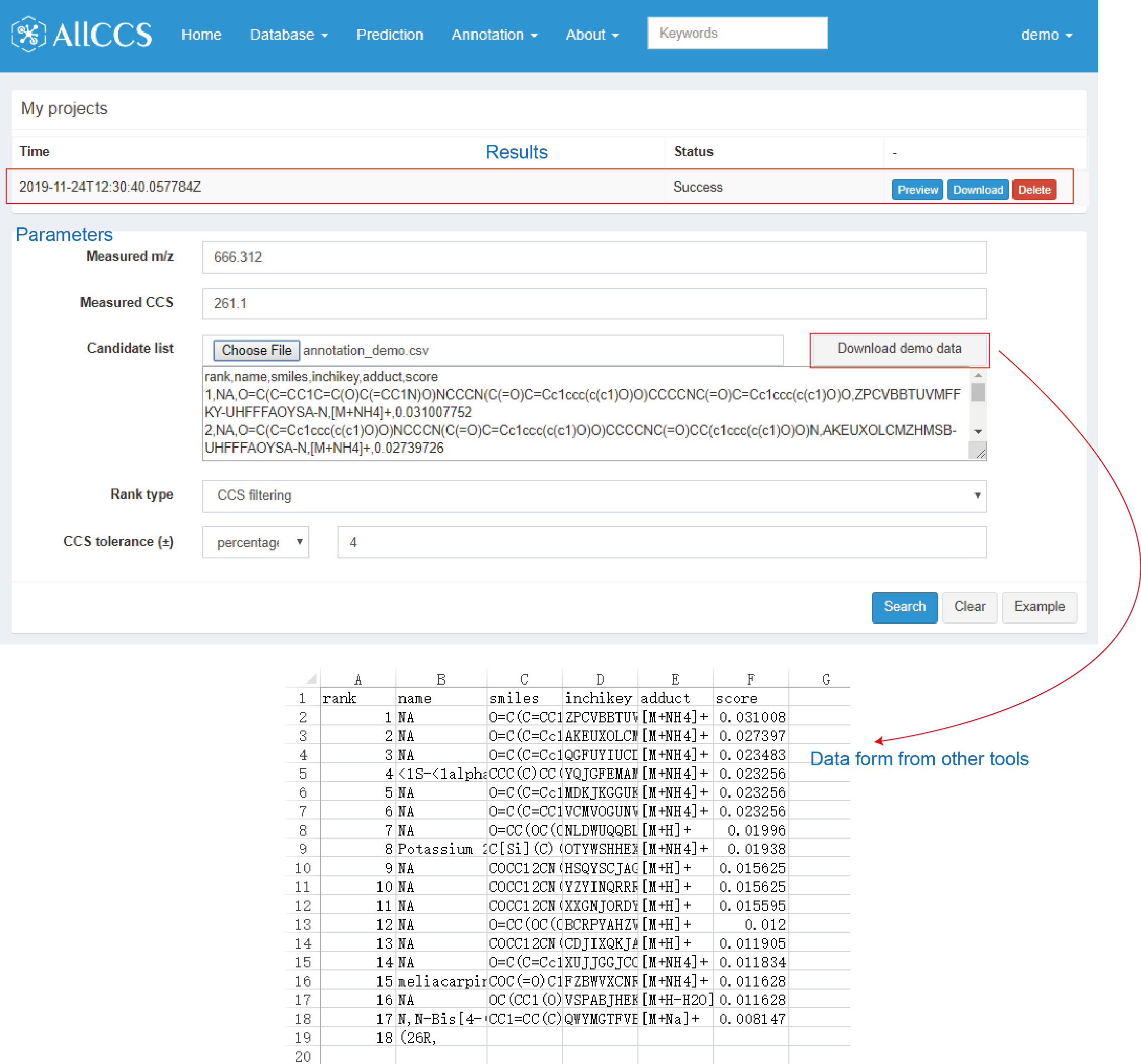
Figure 4.3: Candidate rank function
- rank: The first column in the CSV table. It is the score rank from other tools (e.g. MetFrag, CFM-ID, MS-FINDER, SIRIUS etc).
- name: The second column in the CSV table. Compound names of candidates.
- smiles: The third column in the CSV table. SMILES structures of candidates.
- inchikey: The fourth column in the CSV table. InChIKey identifier of candidates.
- adduct: The fifth column in the CSV table. Adduct form of candidates. Please note that it only supports 7 common adducts (Positive mode, [M+H]+, [M+Na]+, [M+NH4]+, [M-H2O+H]+; Negative mode, [M-H]-, [M+Na-2H]-, [M+HCOO]-).
- score: The sixth column in the CSV table. The MS/MS match score generated in in-silico MS/MS tools.
Note:
- The inputted CSV file should have the same column name with demo data.
- The column order should be keep same with demo data.
4.2.2 Parameter setting
In the candidates rank function, users can get more reliable results by adjusting parameters according to their experiments. The candidate rank function contains parameters as follows:
- Measured m/z: Experimental m/z of corresponding feature.
- Measured CCS: Experimental CCS of corresponding feature.
- Candidate list: A CSV file of candidate (See Section 4.2.1).
- Rank type: It consists of CCS filtering and CCS scoring. When choosing CCS filtering, the next option is CCS tolerance (Figure 4.3). It will filter the results that out of the pre-defined CCS tolerance. If you choose CCS scoring, the follow options are showed as Figure Figure 4.4. It consists of Minimum tolerance, Maximum tolerance, CCS weight, and MS/MS weight.
- CCS tolerance (±): This parameter is available in CCS filtering. The tolerance between experimental CCS and theoretical CCS in database. Users can choose percentage or Å2 as unit.
- Minimum tolerance (%): This parameter is available in CCS scoring. If error is within the tolerance, CCS match score equals to 1. Range: 0-10.
- Maximum tolerance (%): This parameter is available in CCS scoring. If error is larger than the tolerance, CCS match score equals to 0, and lipid candidates will be removed. Range: 0-20.
- CCS weight: This parameter is available in CCS scoring. The CCS match score weight to calculate integrated score.
- MS/MS weight: This parameter is available in CCS scoring. The MS/MS match score weight to calculate integrated score.
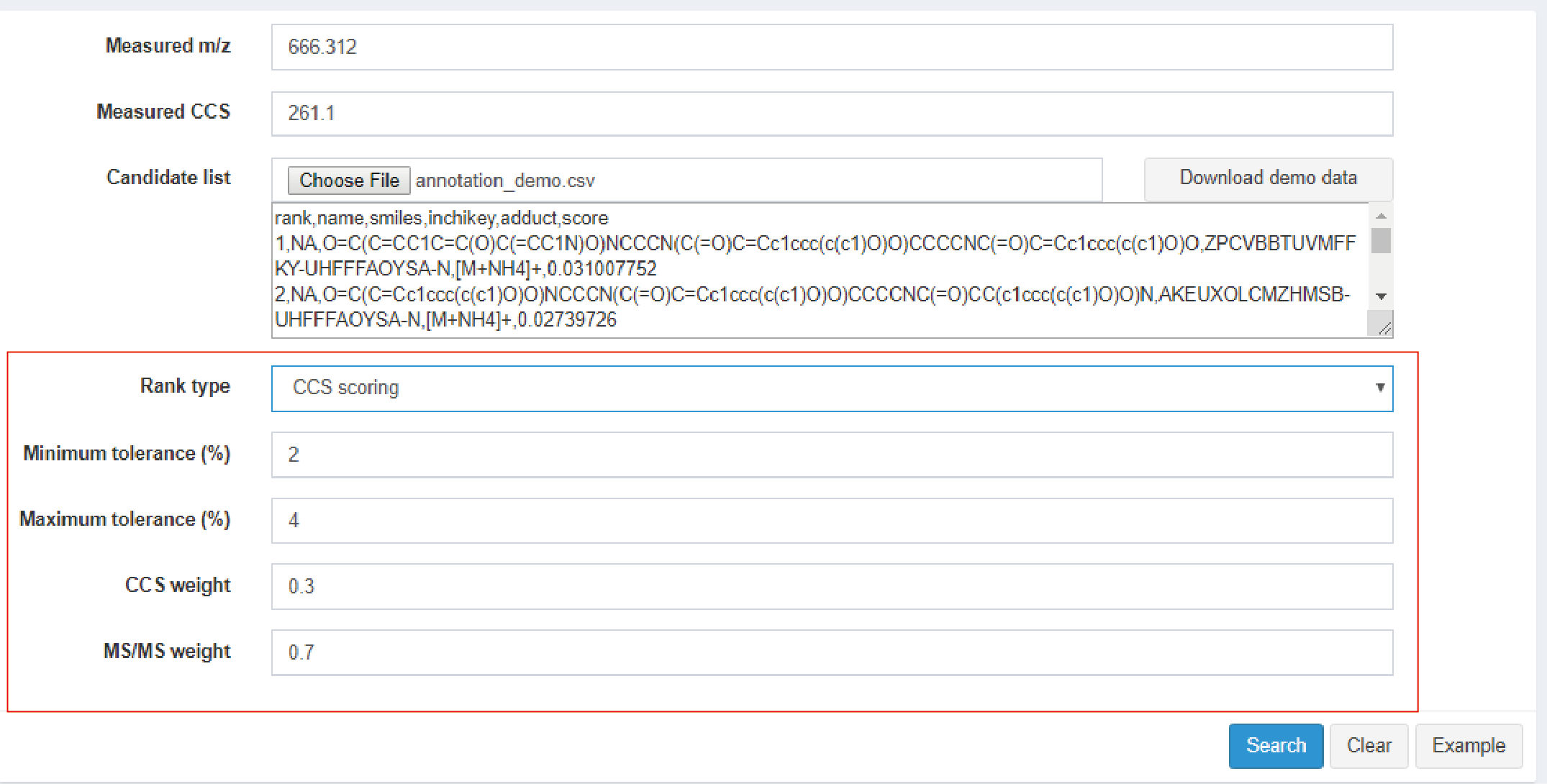
Figure 4.4: CCS scoring
4.2.3 Results
Results of user submission are showed in the “My projects” panel (Figure 4.2).
4.2.3.1 CCS filtering
Users can get the detailed information of candidates by clicking the browser button (Figure 4.5). In below text, it contains brief information for each candidate.
- Rank: The new rank after filtering with CCS.
- Name: Consistent with the name in candidate list (see Section 4.2.1).
- SMILES: Consistent with the smiles in candidate list (see Section 4.2.1).
- InChIKey: Consistent with the inchikey in candidate list (see Section 4.2.1).
- Adduct: Consistent with the adduct in candidate list (see Section 4.2.1).
- MS/MS score: Consistent with the score in candidate list (see Section 4.2.1).
- MS/MS rank: Consistent with the rank in candidate list (see Section 4.2.1).
- Predicted CCS (Å2): The predicted CCS with SMILES and InChIKey.
Users can also click download to obtain CSV table which contains the same information as preview results (Figure 4.5).
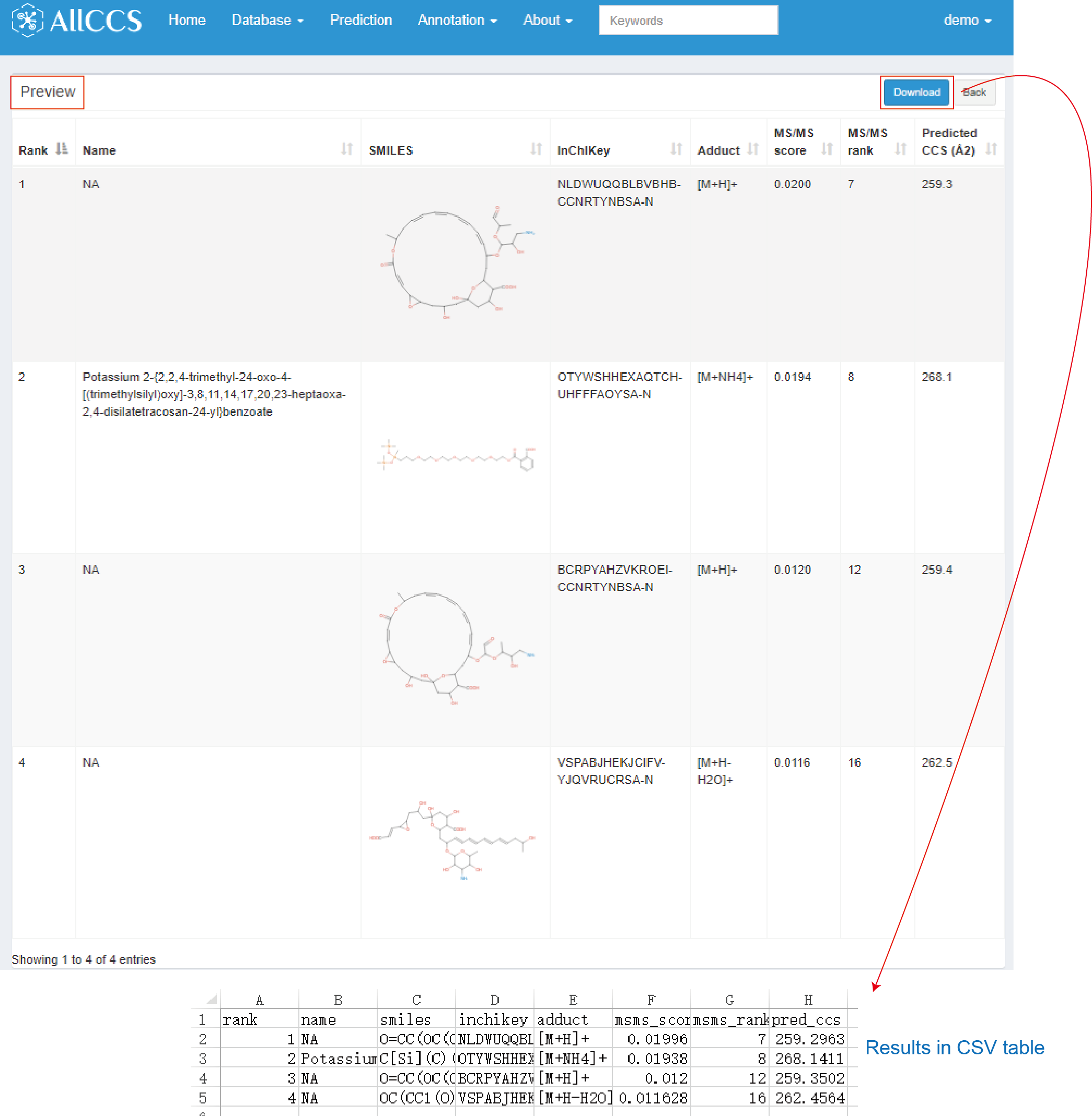
Figure 4.5: CCS filtering result of candidates
4.2.3.2 CCS scoring
The results generated with CCS scoring function are similar with results from CCS filtering (Figure 4.6). The difference is that CCS scoring has two additional columns as CCS score and integrated score.
- CCS score: CCS score generated by comparing experimental CCS to predicted CCS values. CCS match is scored using a trapezoidal function. (The detail of trapezoidal function LipidIMMS Analyzer (Zhou et al. 2019))
- Integrated score: The integrated score is calculated using a linear weighting function according to the user-defined weight for each match score.
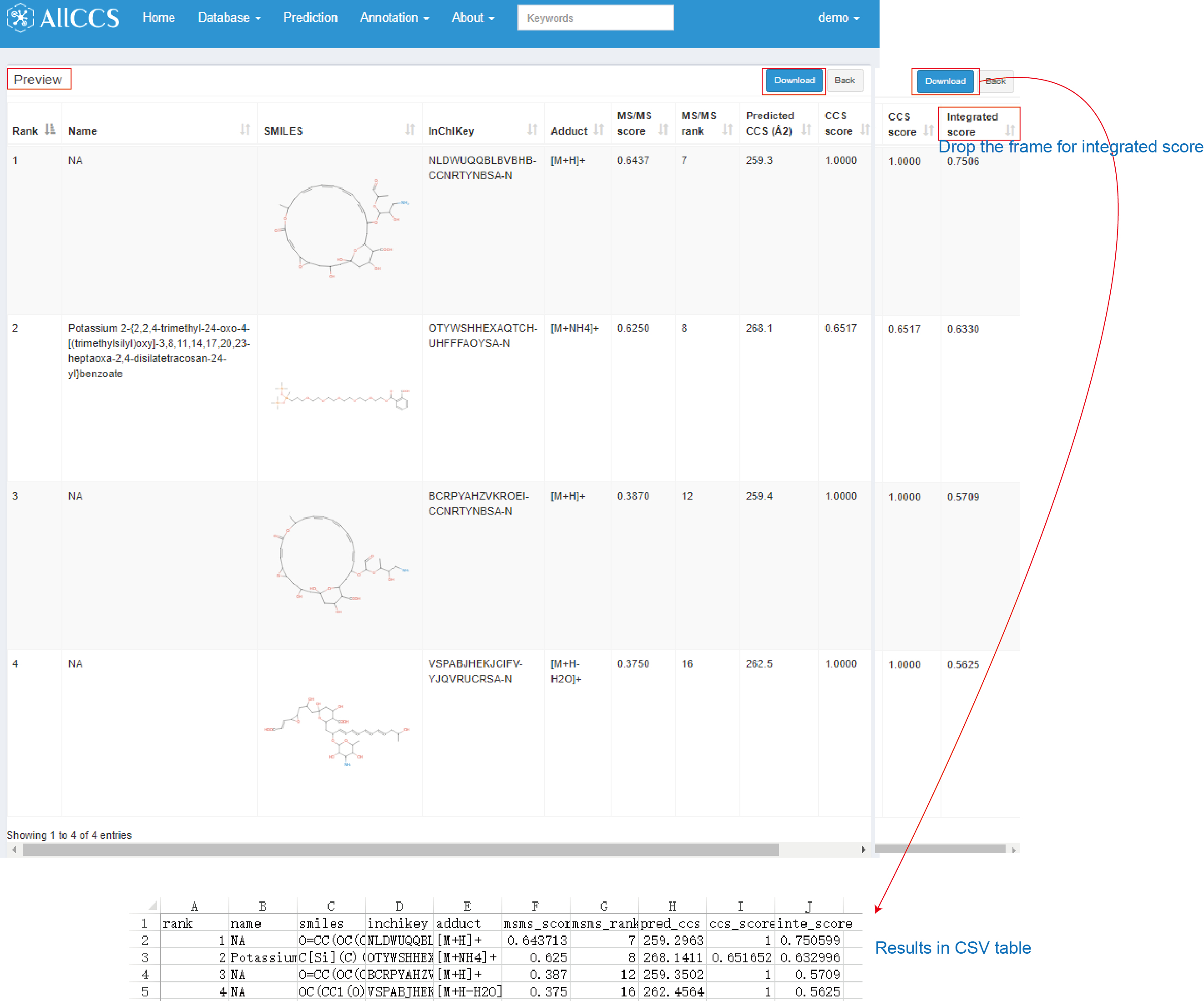
Figure 4.6: CCS scoring result of candidates
References
Zhou, Zhiwei, Xiaotao Shen, Xi Chen, Jia Tu, Xin Xiong, and Zheng-Jiang Zhu. 2019. “LipidIMMS Analyzer: Integrating Multi-Dimensional Information to Support Lipid Identification in Ion Mobility-Mass Spectrometry Based Lipidomics.” Bioinformatics, 698–700. doi:10.1093/bioinformatics/bty661.